- Flange (Shoulder)
An external rib or lip machined on most pin, receptacle, and spring pin components that is typically the largest external diameter. Most often located on one end of the part but can also be found near the center in certain designs. Its primary function is to assist in board assembly by orienting the product in the mounting hole and providing added support during solder or press-fit mounting. In spring pin and receptacle products, this feature also plays a pivotal role in the assembly of the component.
- Spring Rate
The spring rate of a spring will be determined by spring material, diameter of the material, and number of coils per the spring length.
- Side Load
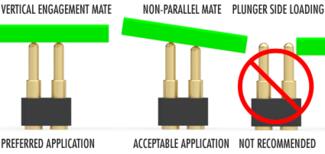
A horizontal or lateral force that is applied to a component. Most often referring to spring-loaded products, which involves a sliding/swiping action exerted to the plungers. While a certain degree of lateral/non-vertical engagement is possible for spring pins, excessive side loading can compromise the expected life of the product.
- Electromechanical
To relate to or involve an electrically operated mechanical device
- Interconnect
Connector products comprised of pins, receptacles or spring pins loaded pins into an insulated housing, designed to form a permanent or cyclable electrical connection with a corresponding mate. Pin + receptacle connections are made using a male header in combination with a female socket, commonly offered in SIP and DIP style packaging. This differs from spring-loaded interconnect pairs, where a spring-loaded header is mated with a target connector. Applications include board-to-board connections, along with wire-to-board, device-to-board, cable-to-board, and board stacking operations. Learn More
- Press-Fit
A solderless mechanical connection between a machined feature on an interconnect component and its corresponding mounting hole on the board/housing. These features are comprised of tapered cuts or serrations with a slightly larger diameter than the mounting hole to provide a frictional fit-up when the component is driven in. Mounting hole size and style dictate the appropriate feature to select. For example, barb (fishhook) & knurl features are suited for non-plated through holes, while hex & square features are designed for mounting in plated though holes. Learn More
- Misalignment
Defined as incorrect or poor alignment between mating components, features, or products within an interconnect system. It can occur in pin & receptacle connections when the mating pin inserted at an aggressive angle. It can also occur in spring-loaded connections by exposing the plunger of the spring pin to a lateral or side load. While a small amount of misalignment is to be expected and acceptable during a mated connection, an excessive amount can cause significant damage to the mating components. This damage may present itself in the form of reduced component performance and/or premature failure.
Pin/Receptacle Misalignment Spring-Pin Misalignment
- Operating Temperature
The specified timeframe and temperature range by which a part or device can safely function within. Applications should ensure staying within these limits for optimal performance and durability.
- Spring Force
The amount of force required to compress the plunger of a spring pin to a specified distance. This characteristic is primarily driven by the spring component, namely its design and base material. The spring forces specified for Mill-Max spring-loaded products refer to plunger compression at .
- Mounting Hole Size
Size call out for the mounting holes.