- Mounting Tab
A tab-like feature included on the ends of select insulated housings to allow for further mechanical retention to the PCB. These features include a hole that can either be provided bare to allow for addition of application specific hardware, or prepopulated with a threaded insert to allow for fastening with a screw or comparable threaded component. View Examples
- Turret
A feature on a pin or receptacle which consists of a post machined with a singular or series of larger diameter heads. The primary purpose of this feature is to facilitate wire termination by providing a surface to wrap and solder a wire to the component. View Examples
- Insulator
- A molded or machined plastic dielectric housing which retains a single interconnect component or a multi-position array in a connector assembly. Depending on the requirements of the application, these housings can have different external dimensions, footprint patterns, and include additional features such as a cut-out window, stand-offs, or alignment pegs. Mill-Max typically uses molded plastic insulators for standard connector products, but has the capabilities to provide customer driven solutions with either molded or machined plastic housings.
- Mounting Hole
Hole(s) on a board, housing, or insulator used for the retention of a pin, receptacle, spring pin, or connector. Can be plated or left bare depending on the application or type of housing/part. The most critical specification for this feature is the diameter/hole size.
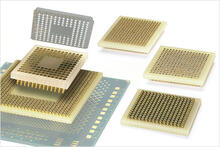
- Ball Grid Array (BGA)
A surface mount packaging for integrated circuits (ICs) such as microprocessors. The bottom of the package features a high-density array of solder balls or preforms to make connections to a PCB. Mill-Max offers a two-piece adapter system for making BGA devices pluggable; This consists of a male header which mounts to the preforms on the underside of the BGA, as well as a female socket to mate with the header. Standard pitch options are .8mm, 1mm, and .050”. Learn More
- Threading
The defining feature of screws, nuts, and bolts which consist of grooved helical ridges wrapped around a cylinder. Threads are used to mount components onto a board or housing without the use of solder or an adhesive, or for fastening two components together for added mechanical rigidity. A threaded connection requires one component to be machined with exterior threads, allowing it to be torqued into a mating component with corresponding interior threads. The features that support threaded mounting can be found on both discrete and connector-based solutions. View Examples
- Tape & Reel
Component packaging suited for use with automated pick & place equipment. Parts are housed on a continuous tape strip, each one placed inside a formed pocket based on the part’s specific design and dimensions. Adjacent pockets are spaced at a consistent distance, referred to as the pocket pitch. The cavities are further secured by a cover tape placed over the top. The entire carrier tape strip is wound up onto a reel for easy loading into a pick & place machine. Learn More
- Stroke/Travel
- The specified distance by which the plunger of a spring pin compresses when being cycled. Each spring pin is rated for a maximum stroke distance, starting from the product at its initial height in a completely uncompressed state. As a general recommendation, between 25% and 75% of the max. stroke should be used for optimal electrical and mechanical performance. Excessive compression of the plunger past the max. stroke value (over-compression) can jeopardize performance and cause premature failures. Learn More. See operating travel range for more information on stroke/travel.
- Profile
With electrical components, the profile typically refers to height of the part above the board after assembly. PCB assemblies can require multiple stacked boards set at fixed distances on top of each other, which may limit what the height of an individual component or a set of mated components can be. Designs which require flush components without any protrusion on top of the board are referred to as zero profile applications. Ultra-low and low-profile applications attempt to conserve board height by using short, compact components with minimal mated height. Mid and high-profile applications exist as well, with “board stacking” header/socket mates being used to actually add more height by “filling in the gaps” between two boards with a mated set.
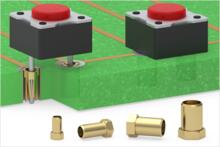
- Power Spring-Loaded Pin
Mill-Max spring pins that offer a higher current rating and larger overall diameters when compared to our typical spring pin products. The added size and robustness make them ideal for applications that require a more rugged interconnect solution, such as ones with rough or punishing environments. Power spring pins are offered discrete in through-hole solder tail, surface mount, solder cup and crimp mounting styles, as well as in assembled connectors with rugged insulator housings. View Examples